Hand surgery is not usually considered by the general public to be part of plastic surgery. However, plastic surgeons have contributed to hand surgery since its inception, and hand surgery training is an integral part of all plastic surgery training programs in the United States. Nearly half of all hand surgery procedures in the U.S.A. are performed by plastic surgeons.
Dr. Kind completed a fellowship in Hand and Microsurgery, and received accreditation from the American Board of Surgery with a Certificate of Added Qualification in Surgery of the Hand. Dr. Kind is a member of the American Society for Surgery of the Hand.
Hand Surgery problems treated by Dr. Kind include many common problems such as fractures and tendon injuries, carpal tunnel syndrome, Dupuytren’s disease, ganglion cysts, arthritis, and tendonitis. In addition, Dr. Kind has extensive experience with the care of complex post-traumatic injuries such as joint replacement and tendon and nerve reconstruction. Dr. Kind helped introduce the two-piece joint for total replacement of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints, and has extensive experience with all types of arthroplasty in the hand and wrist.
Arthritis
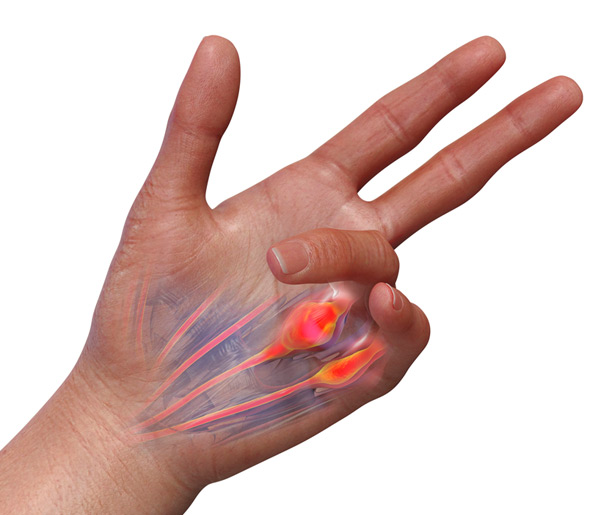
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome involves a minimally invasive procedure to relieve pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. This technique uses small incisions and specialized instruments to cut the transverse carpal ligament, which is compressing the nerve. The benefits of microsurgery include reduced scarring, less postoperative pain, and quicker recovery times. This precise approach allows for effective symptom relief, restoring hand function and alleviating numbness, tingling, and pain associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. This can be done under local anesthesia in the office, or in a surgery center.
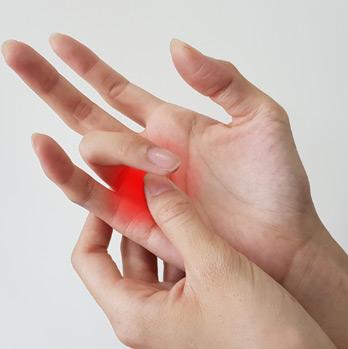


Dupuytren’s Disease
Dupuytren’s Disease may be treated by fasciectomy to excise the thickened diseased cords in the palm that cause finger contractures. Using high-power magnification and fine instruments, the surgeon carefully removes or separates the fibrous tissue, allowing the fingers to straighten and improve hand function. This minimally invasive approach reduces recovery time and scarring compared to traditional surgery. The goal is to restore mobility and reduce deformity, enhancing the patient’s ability to perform daily activities.
Patients may undergo surgery to treat ganglion cysts. The procedure involves the precise removal of the cyst and its stalk using small incisions, magnification, and specialized instruments. The procedure effectively removes the cyst, alleviating symptoms such as pain and discomfort, and minimizes the risk of recurrence. By carefully excising the cyst and its root, this surgery helps restore normal function and appearance to the affected area.
Tendonitis may be treated with surgery using specialized instruments to make small incisions and repair the inflamed or damaged tendon. This technique precisely removes the damaged tissue, promotes healing, and restores function. The minimally invasive approach reduces recovery time, minimizes scarring, and lowers the risk of complications compared to traditional surgery. Surgery for tendonitis is considered when conservative treatments fail, providing significant pain relief and improving the affected tendon’s performance and strength.
Microsurgery for post-traumatic injuries, including blood vessel and nerve repair and reconstruction, utilizes advanced, minimally invasive techniques to repair and restore function. Joint replacement involves precisely fitting prosthetic components, while tendon and nerve reconstruction repairs damaged tissues to regain mobility and sensation. This approach reduces recovery time, minimizes scarring, and enhances overall outcomes by promoting more accurate and efficient healing compared to traditional surgical methods, ultimately improving patients’ quality of life and functional abilities.