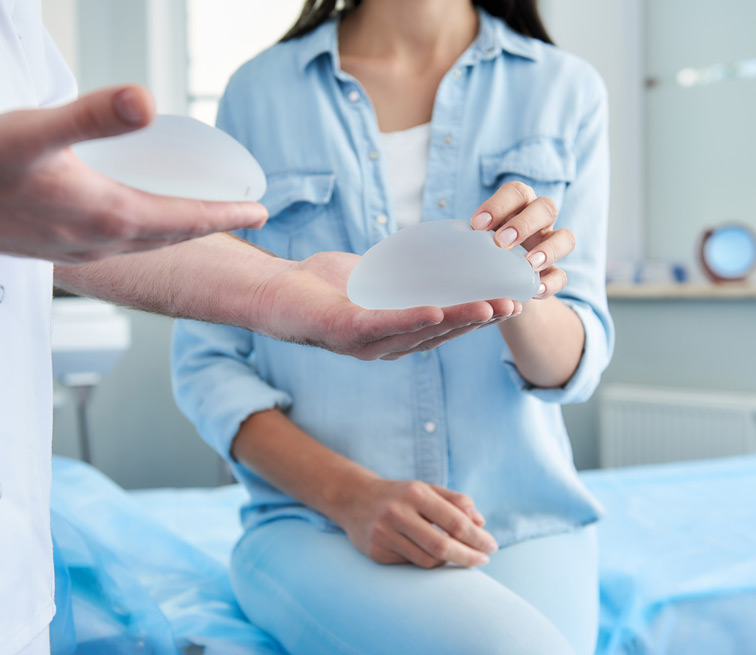

Implant reconstruction surgery is a procedure that uses implants to rebuild a breast following mastectomy or lumpectomy using breast implants. The implants can be filled with saline or silicone gel and are placed either directly under the skin or, less commonly, beneath the chest muscle. This method can be done in one or two stages: immediate reconstruction, where the implant is placed during the mastectomy, or delayed reconstruction, which involves a tissue expander initially and implant placement at a later date.
Implant reconstruction is a common choice for women looking to restore their breast contour and appearance after breast cancer surgery. This technique offers a relatively straightforward and less invasive option for women who are not candidates for flap reconstruction or prefer not to use their own tissue for reconstruction.
Benefits of Implant Reconstruction
Implant reconstruction offers several benefits, including a shorter surgery and recovery time compared to flap reconstruction. It avoids the need for tissue harvesting from other parts of the body, reducing potential donor site complications. Implants provide a predictable shape and size, which can be easily adjusted to match the patient’s desired appearance. Additionally, implant reconstruction can be combined with other breast surgeries, such as lifts or reductions, to achieve optimal aesthetic results. This method can significantly improve self-confidence and body image after breast cancer treatment.
How Implant Reconstruction is Done
Implant reconstruction can be performed immediately during the mastectomy or as a delayed procedure. If delayed, a tissue expander is placed beneath the skin or the chest muscle to gradually stretch the skin and/or muscle over several weeks. Once the desired expansion is achieved, a second surgery is performed to replace the expander with a permanent implant. If immediate reconstruction is chosen, the implant is inserted directly at the time of mastectomy. Incisions are closed, and the reconstructed breast is bandaged for healing.


Who Implant Reconstruction Surgery is For
Implant reconstruction is suitable for women who have undergone mastectomy or lumpectomy and desire to restore their breast shape and contour. It is ideal for those who prefer not to use their own tissue for reconstruction or do not have enough tissue available for flap procedures. It is important for individuals to have realistic expectations and understand the potential risks and benefits.
Surgical Process
The treatment process for implant reconstruction begins with a consultation with a plastic surgeon to discuss goals, options, and potential risks. If immediate reconstruction is planned, the implant is placed during the mastectomy. For delayed reconstruction, a tissue expander is inserted under the chest muscle and gradually filled over weeks to stretch the skin. Once expansion is complete, a second surgery replaces the expander with a permanent implant.


Q: What is the recovery time after implant reconstruction surgery?
A: Most patients can return to normal activities within four to six weeks. Full recovery and the final appearance of the reconstructed breast may take several months.
Q: Are there risks associated with implant reconstruction surgery?
A: Risks include infection, implant leakage or rupture, capsular contracture, and complications from anesthesia. Choosing an experienced surgeon and following post-operative care instructions can help minimize these risks.
Whenever an implant of any kind is placed in the body, a layer of scar tissue forms around the implant. This “capsule” varies in thickness, and can sometimes calcify and become hard. This is referred to as “capsular contracture”. The occurrence of capsular contracture is a concern with implant reconstruction. As a result of capsular contracture, implant reconstructions become more firm and can remain somewhat immobile, especially compared to a normal breast. If a patient has had radiation or is planning to have radiation, implant reconstruction is usually discouraged because of high rates of capsular contracture and other complications.
Another disadvantage of implants is the fact that there is a recognized leak or rupture rate. According to the implant manufacturers, the life expectancy of an implant is approximately 10 years.




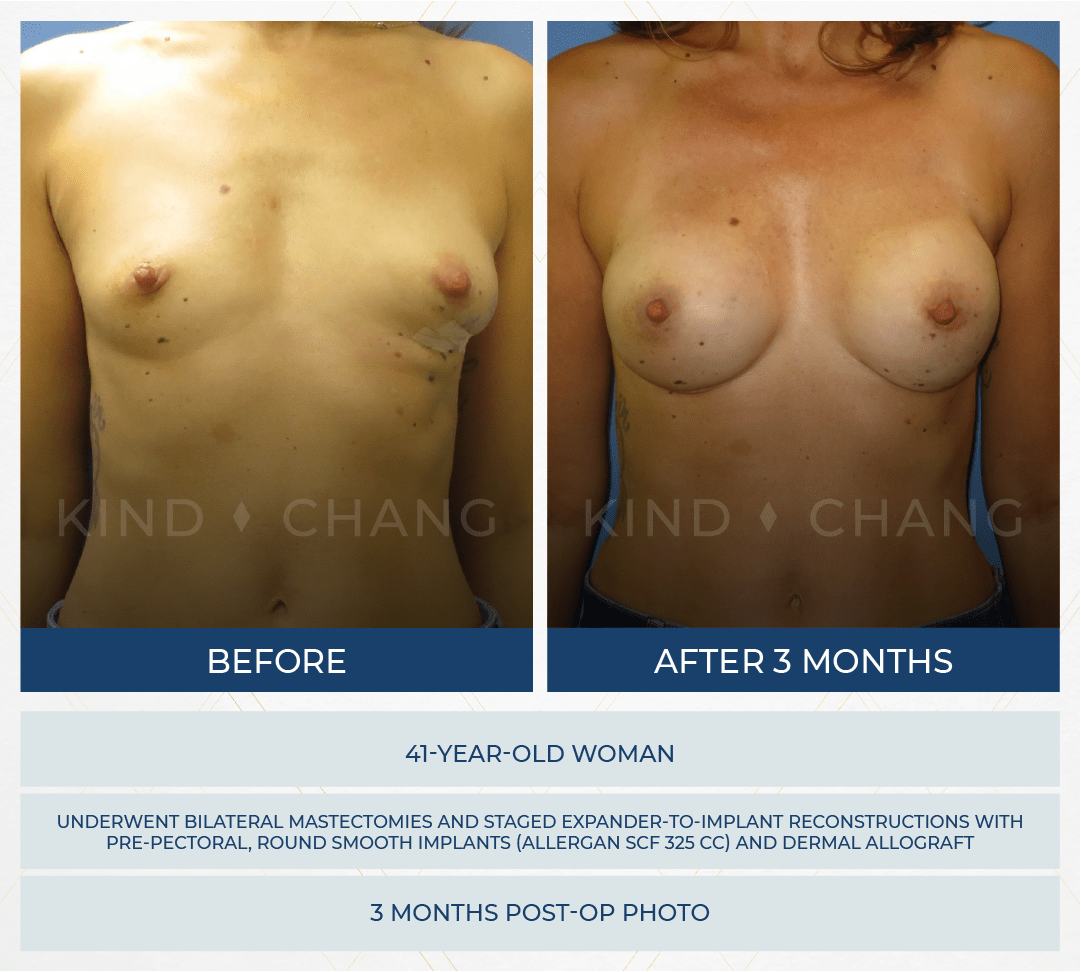
DISCLAIMER: Before and after results are NOT a guarantee that your results will be the same or similar. Each patient’s results will be different. Your results will vary from other patient’s results.
